
Call
+61 7 4631 2589
1800 063 632 (free call within Australia)
Virtual Help Desk (Zoom)
Open access (OA) is a set of principles and a range of practices through which research outputs are distributed online, free of cost or other access barriers. Through licensing via an open license (usually a Creative Commons License), freely available outputs can also be legally shared and reused. Hence, open access is more than just free access (Open Access Australasia, 2024).
The original definitions of open access were first proposed in Budapest in 2002, Berlin in 2003, and Bethesda in 2003.
"By open access to this literature, we mean its free availability on the public internet, permitting any users to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to the full texts of these articles, crawl them for indexing, pass them as data to software, or use them for any other lawful purpose, without financial, legal, or technical barriers other than those inseparable from gaining access to the internet itself. The only constraint on reproduction and distribution, and the only role for copyright in this domain, should be to give authors control over the integrity of their work and the right to be properly acknowledged and cited." (Budapest Open Access Initiative Declaration, 2002)
Open access publications are immediately and easily accessible free of charge and reusable. This expedites the scholarly communication process, enhancing efficiency in research and innovation. It fosters international and interdisciplinary collaboration between the networking researchers. Open access significantly increases the citation frequency and also the visibility of research findings. Authors retain their rights to exploit the works instead of assigning these rights to a publisher. An open access publication can be redistributed and reused easily by others. (Open Access Network, 2023)
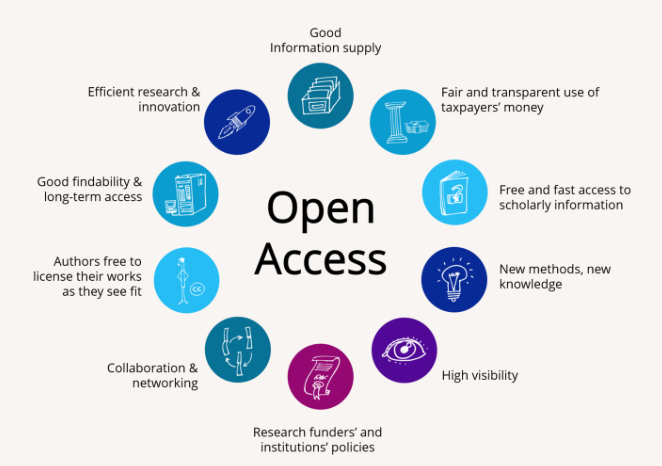
Source: based on Brinken, H. (2021). 10 Gründe für Open Access. Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4643859 (CC BY 4.0 International)
Recent articles on the benefits of open access: